Interactive and interactional metadiscourse markers in research articles of Indonesian expert writers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v6i1.1082Keywords:
metadiscourse, interpersonal marker, interactive marker, research article, expert writerAbstract
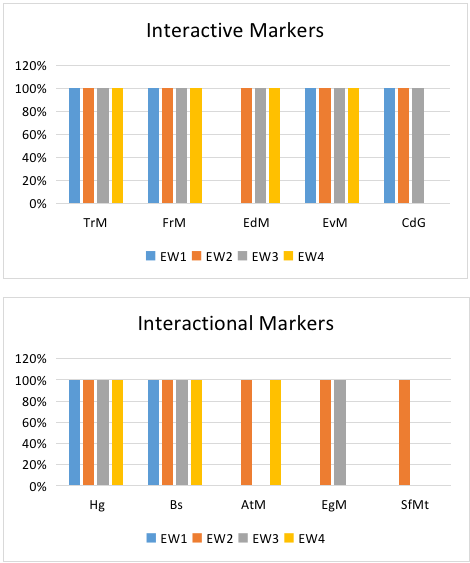
Academic writing articles serve as the medium of communication among scholars to share knowledge and new inquiries and are made in such a way that the idea they deliver is both understandable and accepted. One essential action to accomplish this is by employing metadiscourse markers. Metadiscourse is viewed as an essential element of credible written texts created by students of ESL and native speakers, by which the intelligibility of communication in research articles can be accomplished through suitable discipline conscience, norms, and belief to track the writers’ pathway to academic promotions. Therefore, employing descriptive qualitative approach, this study aims at investigating the utilization of interpersonal metadiscourse markers and their functions in academic writing. Analysing discussion section of research articles written by Indonesian expert writers, the results show that the metadiscourse markers in the articles are found to be similar to the commonly used markers among academic community, including interactive and interactional markers. Moreover, the employment of markers in the articles reveal the functions of them to indicate relation between sentences, involvement of readers, existence of example, limitation of commitment to propositions, emphasis on general practice and certainty, and reference to the writer.
HIGHLGHTS:
- The appropriate utilization of interactive and interactional metadiscourse markers in research articles indicates the international norm of academic writing.
- The Indonesian expert writer articles fulfill the intelligibility of communication in international research articles.
- The writing course in the universities needs to emphasize the essential functions of metadiscourse markers.
Downloads
References
Akil, M. (2011). The quality of Indonesian—English translation by English Depart- ment students of higher learning institution in Makassar. The quality of Indonesian-English translation by English Department students of higher learning institution in Makassar. Linguistika, 18:1–14.
Akbari, R. and Yazdanmehr, E. 2014. A Critical Analysis of the Selection Criteria of Expert Teachers in ELT. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 4 (8): 1653-1658.
Amiryousefi, M. and Rasekh, A. E. Metadiscourse: Definitions, Issues and Its Implications for English Teachers. English Language Teaching 3(4): 159-167.
Ary, D., Jacob, L. C., Razavieh, A., & Sorensen, C. 2010. Introduction to Research in Education. (8th Ed). Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth.
Barley, S. 2011. Academic Writing: A Handbook for International Students (Third edition). New York: Routledge.
Firoozian, A., Khajavy, H., and Vahidnia, F. 2012. A Contrastive Study of Metadiscourse Elements in Research Articles Written by Iranian Applied Linguistics and Engineering Writers in English. English Linguistics Research, 1(1): 88-96.
Gholami, J., Nejad, S. R., and Pour, J. L. 2014. Metadiscourse Marker Misuses: A Study of EFL Learners' Argumentative Essays. Procedia- Social and Behavioural Science, 98: 580-589.
Hyland, K. 2005. Metadiscourse: Exploring Interaction in Writing. London: Continuum.
Hyland, K. 2010. Metadiscourse: Mapping Interactions in Academic Writing. Nordic journal of English Studies 9 (2): 125-143.
Johnson, B. and Chistensen, L. 2014. Educational Research: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Approaches. Fifth edition. United State: Pearson Education, Inc.
Khedri, M., Ibrahimi, S. F. and Chang, S. H. 2013. An exploration of interactive metadiscourse markers in academic research article abstracts in two disciplines. Discourse Studies 15(3):319-331.
Kruse, O. 2012. Writing Cultures and Student Mobility. In M. Torrance et al. (Eds.), Learning to write effectively: Current trends in European research(pp. 293- 296). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing.
Lestari, L. A. 2008. The Interactional Approach to the Teaching of Writing and Its Implications for Second Language Acquistion. TEFLIN Journal, 19(1): 42-56.
Letsoela, P. M. 2013. Inappropriate Use of Transitions by National University of Lesotho Students. International Journal of English Language Education, 2 (1): 100-112.
Lin, C. 2005. Metadiscourse in Academic Writing: An Investigation of Graduate Students’ MA Theses in Taiwan. Taiwan Journal of TESOL, 2 (1): 1-66.
Livingstone, K. A. 2019. Examining the Use of Metadiscourse Markers in Academic Writing. International Journal of Literature, Language and Linguistics, 5 (3): 244-254.
Mazic, I. 2013. The Importance of Proper Citation of References in Biomedical Articles. Acta Informatica Medica 21(3):148-55.
Oshima, A and Hogue, A. 2007. Introduction to Academic Writing (Second Ed.). New York: Pearson Education, Inc
Shafique, H., Shahbaz, M., and Hafeez, M. R. 2019. Metadiscourse in Research Writing: A Study of Native English and Pakistani Research Articles. International Journal of English Linguistics, 9 (4): 376-385
Wijaya, M. H. 2010. Flouting and Hedging in the Graduate Student’s Classroom Discussion Context at State University of Malang. Unpulished Master Thesis. Malang: Library of State University of Malang
Zarei, G.R., & Mansoori, S. 2011. A contrastive study on metadiscourse elements used in humanities vs. non-humanities across Persian and English. Journal of English Language Teaching, 4(1), 42 -50.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Dian Kustyasari , Yazid Basthomi, Mirjam Anugerahwati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







