Self-organized learning environment teaching strategy for ELT in Merdeka Belajar concept for high school students in Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v5i2.869Keywords:
SOLE teaching strategy, freedom to learn, TEFL, merdeka belajarAbstract
As the development of the industrial revolution takes place, disruptions are happening constantly in almost every major sector of the current industries. Companies and organizations complained about the competencies of the graduates entering the work force. This matter questions the readiness of the education system in preparing the students for the real world. Problems in education such as the regulations, strict policies and instructions from the government are undermining the role of the teachers to do what they think best for their students. This standardization has harmed the motivation and enthusiasm to learn, especially in English language class. Lack of motivation and English Language competency could harm students’ opportunity in accessing the vast global network of knowledge. Merdeka Belajar and SOLE are the promising alternatives in improving ELT. This article is somewhat a position paper trying to clear one side of a debatable opinion about a hot issue. It aims to persuade the reader that our opinion is valid and defensible. In doing so, we then separate the discussion into several parts regarding the analysis of concepts of Merdeka Belajar and SOLE (Self-Organized Learning Environment) related to ELT and motivation in language learning, as well as innovation in education.
HIGHLIGHTS:
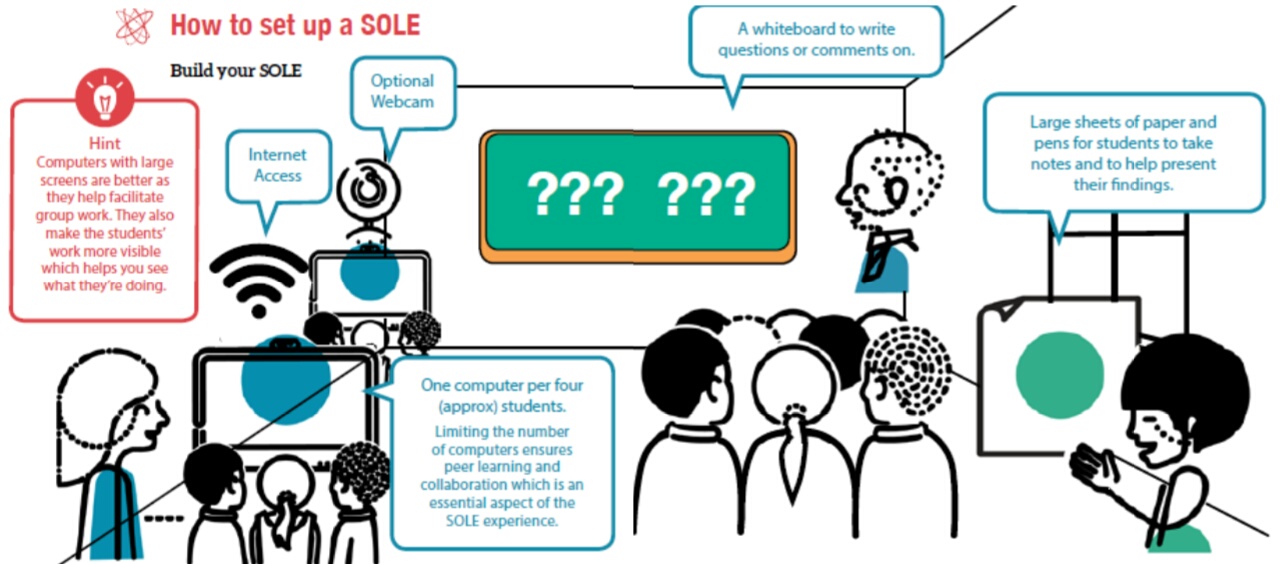
- SOLE (Self-Organized Learning Environment) is a concept developed by Sugata Mitra, and the researchers at the SOLE Centre in Newcastle University.
- SOLE with its highly influenced Constructivism approach lets the learners to take steer of their learning process gives them the ability to make meaning of the subject on their own.
- Merdeka Belajar (Freedom to Learn) is a new concept that needs to be tread carefully to direct the discussion objectively.
Downloads
References
Abidah, A., Hidaayatullaah, H. N., Simamora, R. M., Fehabutar, D., & Mutakinati, L. (2020). The Impact of Covid-19 to Indonesian education and its relation to the philosophy of “Merdeka Belajar.” Studies in Philosophy of Science and Education, 1(1), 38–49. https://doi.org/10.46627/sipose.v1i1.9
Al Rifai, N. (2010). Attitude , motivation , and difficulties involved in learning the English language and factors that affect motivation in learning it. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2(2), 5216–5227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.849
Anderson, J., Rainie, L., & Luchsinger, A. (2018). Artificial intelligence and the future of humans. Pew Research Center. Retrieved from https://www.elon.edu/docs/e-web/imagining/surveys/2018_survey/AI_and_the_Future_of_Humans_12_10_18.pdf
Anwar, C. (2017). Flipped classroom in teaching vocabulary to EFL young learners. In Conference Proceedings of The 2nd International Conference 2017 on Teaching English for Young Learners (TEYLIN): Indigenous norms to the coming age of one Asia (pp. 109-115).
Anwar, C., & Pratama, A. (2016). Flipped classroom in teaching speaking to young learners. In Proceeding of The 63rd TEFLIN International Conference" Creativity and Innovation in Language Materials Development and Language Teaching Methodology (Vol. 1, pp. 285-289).
Bartodziej, C. J. (2017). The Concept Industry 4.0: An empirical analysis of technologies and applications in production logistics. Berlin, Germany: Springer Gabler. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-16502-4
Bley-Vroman, R. (1990). What is the logical problem of foreign language learning? Linguistic Analysis, 20(1–2), 3–49. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139524544.005
Dangwal, R., & Kapur, P. (2008). Children’s learning processes using unsupervised “hole in the wall” computers in shared public spaces. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 24(3), 339–354. Retrieved from https://ajet.org.au/index.php/AJET/article/download/1213/440/
Dangwal, R., Sharma, K., & Hazarika, S. (2014). Hole-in-the-Wall learning stations and academic performance among rural children in India. Journal for Multicultural Education, 8(1), 31–53. https://doi.org/10.1108/JME-03-2013-0006
DeBoer, J. (2009). The relationship between environmental factors and usage behaviors at ‘Hole-in-the-wall’ computers. International Journal of Educational Development, 29, 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2008.02.005
Esteban, P. G., & Peart, M. T. (2014). Introducing self-organized learning environments in higher education as a tool for lifelong learning. E-Learning and Intercultural Competences Development in Different Countries, 413–422.
Farenga, S. J., & Ness, D. (2005). Encyclopedia of education and human development. New York: M.E. Sharpe.
Fleming, G. (2019). 5 Steps to writing a position paper. Retrieved August 23, 2020, from https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-write-a-position-paper-1857251
Gardner, R. C. (1988). Attitudes and motivation. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics, 9, 135–148.
Griffin, Patrick, & Care, E. (2015). The ATC21S Method. In Patrick Griffin & E. Care (Eds.), Assessment and Teaching of 21st Century Skills (pp. 3–33). Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9395-7
Griffin, Patrick, Care, E., & McGaw, B. (2012). The changing role of education and schools. In P. Griffin, B. McGaw, & E. Care (Eds.), Assessment and teaching of 21st century skills (pp. 1–15). Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2324-5
Inamdar, P. (2004). Computer skills development by children using “hole in the wall” facilities in rural India. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 20(3), 337–350. Retrieved from https://ajet.org.au/index.php/AJET/article/download/1351/721/
Inamdar, P., & Kulkarni, A. (2007). ‘Hole-In-The-Wall’ computer kiosks foster Mathematics achievement - A comparative study. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 10(2), 170–179. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.2307/jeductechsoci.10.2.170
Larson, L. C., & Miller, T. N. (2011). 21st Century Skills: Prepare students for the future. Kappa Delta Pi Record, 47(3), 121–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/00228958.2011.10516575
Mitra, S. (2005). Self organising systems for mass computer literacy : Findings from the ‘ hole in the wall ’ experiments. International Journal of Development Issues, 4(1), 71–81. Retrieved from http://hole-in-the-wall.com/docs/Paper06.pdf
Mitra, S. (2012). Beyond the hole in the wall: Discover the power of self-organized learning kindle edition. TED Books. Retrieved from https://eprints.ncl.ac.uk/180343
Mitra, S. (2013). Build a school in the cloud. TED2013. Retrieved from https://www.ted.com/talks/sugata_mitra_build_a_school_in_the_cloud?language=en
Mitra, S. (2014). The future of schooling : Children and learning at the edge of chaos. Prospects, 44(4), 547–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11125-014-9327-9
Mitra, S., James, T., Inamdar, P., & Dixon, P. (2003). Improving English Pronunciation: An Automated Instructional Approach. Information Technologies & International Development, 1(1), 75–84. Retrieved from https://itidjournal.org/index.php/itid/article/download/136/6
Mitra, S., Kulkarni, S., & Stanfield, J. (2016). Learning at the edge of chaos: Self-organising systems in Education. In H. E. Lees & N. Noddings (Eds.), The Palgrave International Handbook of Alternative Education (pp. 227–239). https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-41291-1_15
RI. (1989). Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 2 Tahun 1989 Tentang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional, (1), 1–17.
Rotherham, A. J., & Willingham, D. T. (2010). “21st-Century” Skills. AMERICAN EDUCATOR. Retrieved from https://dbweb01.aft.org/sites/default/files/periodicals/RotherhamWillingham.pdf
Serdyukov, P. (2017). Innovation in education: what works, what doesn’t, and what to do about it? Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, 10(1), 4–33. https://doi.org/10.1108/jrit-10-2016-0007
Shihab, N., & Komunitas Guru Belajar. (2017). Merdeka Belajar di Ruang Kelas. Tangerang Selatan: Literati & Kampus Guru Cikal.
Sholichah, A. F. (2019). Pembelajaran Self-organised learning environment (SOLE) dalam Penyelesaian Tugas di SMP Negeri 9 Semarang. Universitas Negeri Semarang. Retrieved from https://lib.unnes.ac.id/33343/
Suprapto, N., Liu, W. Y., & Ku, C. H. (2017). The implementation of multiple intelligence in (Science) classroom: From empirical into critical. Pedagogika, 126(2), 214–227. https://doi.org/10.15823/p.2017.30
TED. (2013). Sugata Mitra creates a school in the cloud. Retrieved from https://www.ted.com/participate/ted-prize/prize-winning-wishes/school-in-the-cloud
Toffler, A. (1970). Future Shock. New York: Random House.
Wimolmas, R. (2012). A survey study of motivation in English language learning of first year undergraduate students at sirindhorn international institute of technology ( SIIT ), Thammasat University. In FLLT Conference Proceedings by LITU (Vol. 2, pp. 904–915). Retrieved from http://litu.tu.ac.th/FLLT2013/www.fllt2013.org/private_folder/Proceeding/904.pdf.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Muhammad Anis, Choiril Anwar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







