Affective and Cognitive Correlates of Reading Comprehension: A Structural Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v9i2.1900Keywords:
decoding skills, english reading comprehension, reading motivation, socio-economic status, vocabulary developmentAbstract
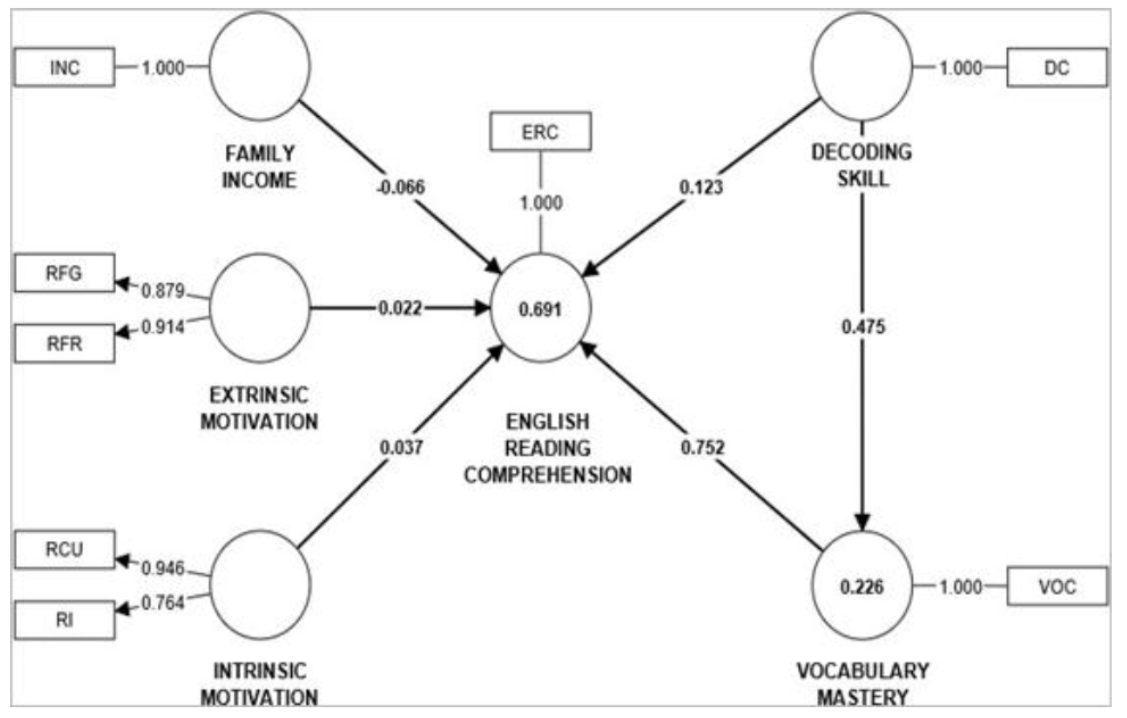
This study investigated the impact of reading motivation, dictation, vocabulary, and socioeconomic status on students’ reading comprehension. A quantitative research methodology was employed, with data collected over four sessions involving tenth-grade students from SMA Yadika Bandar Lampung. The data were gathered through multiple - choice tests, questionnaires, and dictation assessments. The results demonstrated a strong positive correlation between decoding skills and vocabulary in relation to reading comprehension. Statistically significant p-values of 0.000 were found for the relationships between decoding and English reading comprehension (DEC->ERC), decoding and vocabulary (DEC-> VOC), vocabulary and reading comprehension (VOC - >ERC), as well as the combined effects of dictation and vocabulary on English reading comprehension (DEC - >VOC - >ERC). The findings highlight that both dictation skills and vocabulary development play a crucial role in enhancing reading comprehension. In contrast, the study found no significant relationship reading motivation or socioeconomic status and reading comprehension. The correlations betw een extrinsic motivation and English reading comprehension (EM->ERC), intrinsic motivation and English reading comprehension (IM->ERC), and family income and English reading comprehension (INC->ERC) were not statistically significant. These results suggest that while dictation and vocabulary skills are essential for reading comprehension, factors such as reading motivation and socioeconomic status did not exert a significant influence in the study. The findings underscore the importance of focusing on vocabulary and dictation skills to improve students’ reading comprehension, suggesting that targeted educational interventions in these areas could lead to enhanced academic performance for all students. HIGHLIGHTS:-
Impact of Decoding Skills and Vocabulary on Reading Comprehension: The study shows a strong link between students' decoding skills and vocabulary knowledge, which both greatly improve reading comprehension. Decoding directly helps build vocabulary, which then supports reading comprehension. Vocabulary alone accounts for 75.2% of the differences in reading comprehension, emphasizing its key role.
-
Limited Influence of Socioeconomic and Motivational Factors: Unlike some past studies, this research found that socioeconomic status, intrinsic motivation, and extrinsic motivation have little to no impact on reading comprehension. This suggests that cognitive skills, like decoding and vocabulary, are more important for students' reading abilities than socioeconomic or motivational factors.
-
Educational Implications for Curriculum Development: The findings highlight the need to focus on cognitive skills, especially vocabulary and decoding, in reading instruction. Prioritizing these core skills can help educational programs improve students' reading comprehension and close literacy gaps across diverse groups.
Downloads
References
Alvarado, E. S., & Adriatico, C. (2019). Reading Motivation vis-s-vis Academic Performance. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 07(06), 92–106. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2019.76007
Anggia, H., Dharmawan, Y. Y., Cucus, A., & Deviyanti, R. (2023). Student’s reading self-efficacy regression model and differences in online extensive reading program. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2621(1). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0142284
Aro, T., Viholainen, H., Koponen, T., Peura, P., Räikkönen, E., Salmi, P., Sorvo, R., & Aro, M. (2018). Can reading fluency and self-efficacy of reading fluency be enhanced with an intervention targeting the sources of self-efficacy? Learning and Individual Differences, 67, 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2018.06.009
Bradley, R. H., & Corwyn, R. F. (2002). Socioeconomic status and child development. Annual Review of Psychology, 53, 371–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135233
Chen, Q., Kong, Y., Gao, W., & Mo, L. (2018). Effects of socioeconomic status, parent-child relationship, and learning motivation on reading ability. Frontiers in Psychology, 9(JUL). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01297
Coloma, C. J., De Barbieri, Z., Quezada, C., Bravo, C., Chaf, G., & Araya, C. (2020). The impact of vocabulary, grammar and decoding on reading comprehension among children with SLI: a longitudinal study. Journal of Communication Disorders, 86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomdis.2020.106002
Creswell. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
Dey, M. (2021). Psychological processes in language learning and teaching: Scoping review and future research directions. Journal of Psychological Perspective, 3(2), 105–110. https://doi.org/10.47679/jopp.321532021
Efriza, D., Deswarni, D., & Sepyanda, M. (2023). What Can Reading Motivation Do for Improving Student’s Reading Comprehension? Implications for Reading Instruction in the School. ENGLISH FRANCA : Academic Journal of English Language and Education, 7(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.29240/ef.v7i1.4344
Elleman, A. M., & Oslund, E. L. (2019). Reading Comprehension Research: Implications for Practice and Policy. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 6(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/2372732218816339
Fan, Y., Chen, J., Shirkey, G., John, R., Wu, S. R., Park, H., & Shao, C. (2016). Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: an updated review. In Ecological Processes (Vol. 5, Issue 1). Springer Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-016-0063-3
Foorman, B. R., Petscher, Y., & Herrera, S. (2018). Unique and common effects of decoding and language factors in predicting reading comprehension in grades 1–10. Learning and Individual Differences, 63, 12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2018.02.011
Genelza, G. (2022). Phonemic Awareness as Predictor of Word Decoding Ability among Bachelor of Science in Information Technology Students. REiLA : Journal of Research and Innovation in Language, 4(1), 24–40. https://doi.org/10.31849/reila.v4i1.8721
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, Reading, and Reading Disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7(1), 6–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/074193258600700104
Hamilton, D., McKechnie, J., Edgerton, E., & Wilson, C. (2021). Immersive virtual reality as a pedagogical tool in education: a systematic literature review of quantitative learning outcomes and experimental design. Journal of Computers in Education, 8(1), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-020-00169-2
Jonathans, P. M., Widiati, U., Astutik, I., & Ratri, D. P. (2021). The Practices of Intentional Vocabulary Acquisition for Asian EFL Learners: a Systematic Review. English Review: Journal of English Education, 9(2), 253–262. https://doi.org/10.25134/erjee.v9i2.4350
Kazazoğlu, S. (2013). Dictation as a Language Learning Tool. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 70, 1338–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.195
Kim, Y. S. G. (2020). Toward Integrative Reading Science: The Direct and Indirect Effects Model of Reading. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 53(6), 469–491. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219420908239
Kurnaz, H., & Kurnaz, G. (2021). Individual and Socioeconomic Variables as Predictors of Middle School Students’ Intrinsic Reading Motivations. International Journal of Educational Methodology, 7(3), 401–410. https://doi.org/10.12973/ijem.7.3.401
Levesque, K. C., Breadmore, H. L., & Deacon, S. H. (2021). How morphology impacts reading and spelling: advancing the role of morphology in models of literacy development. Journal of Research in Reading, 44(1), 10–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9817.12313
Mar, R. A., Li, J., Nguyen, A. T. P., & Ta, C. P. (2021). Memory and comprehension of narrative versus expository texts: A meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 8, 732–749. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-020-01853-1/Published
Michael, D., & Kyriakides, L. (2023). Mediating effects of motivation and socioeconomic status on reading achievement: a secondary analysis of PISA 2018. Large-Scale Assessments in Education, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40536-023-00181-9
Nanda, D. W., & Azmy, K. (2020). Poor Reading Comprehension Issue in EFL Classroom among Indonesian Secondary School Students: Scrutinizing the causes, impacts and possible solutions. Englisia: Journal of Language, Education, and Humanities, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.22373/ej.v8i1.6771
Ostojić, A. B. (2023). Reading Comprehension Processes: A Review Based on Theoretical Models and Research Methodology. Hrvatska Revija Za Rehabilitacijska Istrazivanja, 59(1), 122–143. https://doi.org/10.31299/hrri.59.1.8
Rech, J. F., & Stevens, D. J. (1996). Variables Related to Mathematics Achievement Among Black Students. The Journal of Educational Research, 89(6), 346–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1996.9941338
Rogelberg, S. L., Starrett, A., Irvin, M. J., & DiStefano, C. (2021). Examining motivation profiles within and across socioeconomic levels on educational outcomes. International Journal of Educational Research, 109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2021.101846
Rogiers, A., Van Keer, H., & Merchie, E. (2020). The profile of the skilled reader: An investigation into the role of reading enjoyment and student characteristics. International Journal of Educational Research, 99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.101512
Rosalina, E. (2019). The Correlation between Self-Esteem and Student’s Reading Comprehension. English Language Teaching Educational Journal, 2(2), 70–78. https://doi.org/10.12928/eltej.v2i2.1190
Röthlisberger, M., Zangger, C., & Juska-Bacher, B. (2023). Matthew effect in vocabulary and reading: A comparison of good and average readers in Grade 1 to Grade 3. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2023.100278
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2020). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: Definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2020.101860
Samuelson, L. K. (2021). Toward a Precision Science of Word Learning: Understanding Individual Vocabulary Pathways. Child Development Perspectives, 15(2), 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12408
Schaffner, E., & Schiefele, U. (2013). The prediction of reading comprehension by cognitive and motivational factors: Does text accessibility during comprehension testing make a difference? Learning and Individual Differences, 26, 42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2013.04.003
Schomaker, M. S., & Zaheer, S. (2014). The role of language in knowledge transfer to geographically dispersed manufacturing operations. Journal of International Management, 20(1), 55–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intman.2013.10.004
Schunk, D. H., & DiBenedetto, M. K. (2021). Self-efficacy and human motivation. In Advances in Motivation Science (Vol. 8, pp. 153–179). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.adms.2020.10.001
Shakir, A., & Ahmad, M. (2020). A Review on the Principles of a Reading Comprehension Test Construction to Assess the Test Takers at Different Levels. Psychology and Education, 57(8), 1920–1302. www.psychologyandeducation.net
Silagi, M. L., Romero, V. U., de Oliveira, M. O., Trés, E. S., Brucki, S. M. D., Radanovic, M., & Mansur, L. L. (2021). Inference comprehension from reading in individuals with mild cognitive impairment. Acta Neurologica Belgica, 121(4), 879–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-019-01264-7
Smith, R., Snow, P., Serry, T., & Hammond, L. (2021). The Role of Background Knowledge in Reading Comprehension: A Critical Review. Reading Psychology, 42(3), 214–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702711.2021.1888348
Stutz, F., Schaffner, E., & Schiefele, U. (2016). Relations among reading motivation, reading amount, and reading comprehension in the early elementary grades. Learning and Individual Differences, 45, 101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2015.11.022
Suk, N. (2021). Developing a sensitive but generalizable measurement of vocabulary gains from self-selected extensive reading. System, 101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2021.102614
Wawire, B. A., & Zuilkowski, S. S. (2021). The role of vocabulary and decoding language skills in reading comprehension: a cross-linguistic perspective. International Multilingual Research Journal, 15(1), 23–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/19313152.2020.1753953
Yang, L., Xiong, Y., & Chen, Q. (2023). The role of linguistic and cognitive skills in reading Chinese as a second language: A path analysis modeling approach. Frontiers in Psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1131913
Zaccoletti, S., Altoè, G., & Mason, L. (2020). The interplay of reading-related emotions and updating in reading comprehension performance. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(3), 663–682. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12324
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Elsa Alfiani, Helta Anggia, Harpain Harpain, Yanuarius Yanu Dharmawan, Dameria Magdalena Sidabalok, Kristóf Lakatos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







