Integrating hybrid learning and team-based project in EFL writing class
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v8i2.1738Keywords:
Integrating, Hybrid Learning, Team-Based Project, Writing, EFL StudentsAbstract
This study aimed to describe the integration of hybrid learning and team-based projects in learning to write and to explain the effectiveness of implementing hybrid and team-based projects in improving students' writing performances. This research method was mixed with quantitative analysis using quasi-experiments and questionnaires, while qualitative analysis used observations in writing classes. The instruments applied were writing tests, questionnaires, and observations. The results of this study were feasible to be used and tested in a small-scale class in the third semester of English Education at the Universitas Muhammadiyah Semarang. The average result of the validation is more than four scores, so it is in the excellent category. Meanwhile, the results of the analysis of student perspectives on learning through Team-Based Projects are divided into four, namely; student perspectives and motivation regarding the implementation of hybrid learning, student perspectives on the effectiveness of Team-Based Projects, student perceptions of independent learning through team-based projects and hybrid learning, and student perceptions about working in groups. All of the indicators were categorized as excellent. In addition, the integration of hybrid learning and team-based project in the English Language Education Study Program with the participation of seventy-two students with the final grades of all students being in the complete category above seventy so that the integration of hybrid learning and team-based projects is effectively implemented in genre text writing classes. Therefore, the results of this study can make a good contribution because they can motivate students to write texts and improve independent student learning.
HIGHLIGHTS:
- Integrating hybrid learning and team-based projects is suitable for use and testing in small class scales in the third semester of English Education at the Muhammadiyah University of Semarang. The average result of the validation results is more than 4.00, so it is in the excellent category.
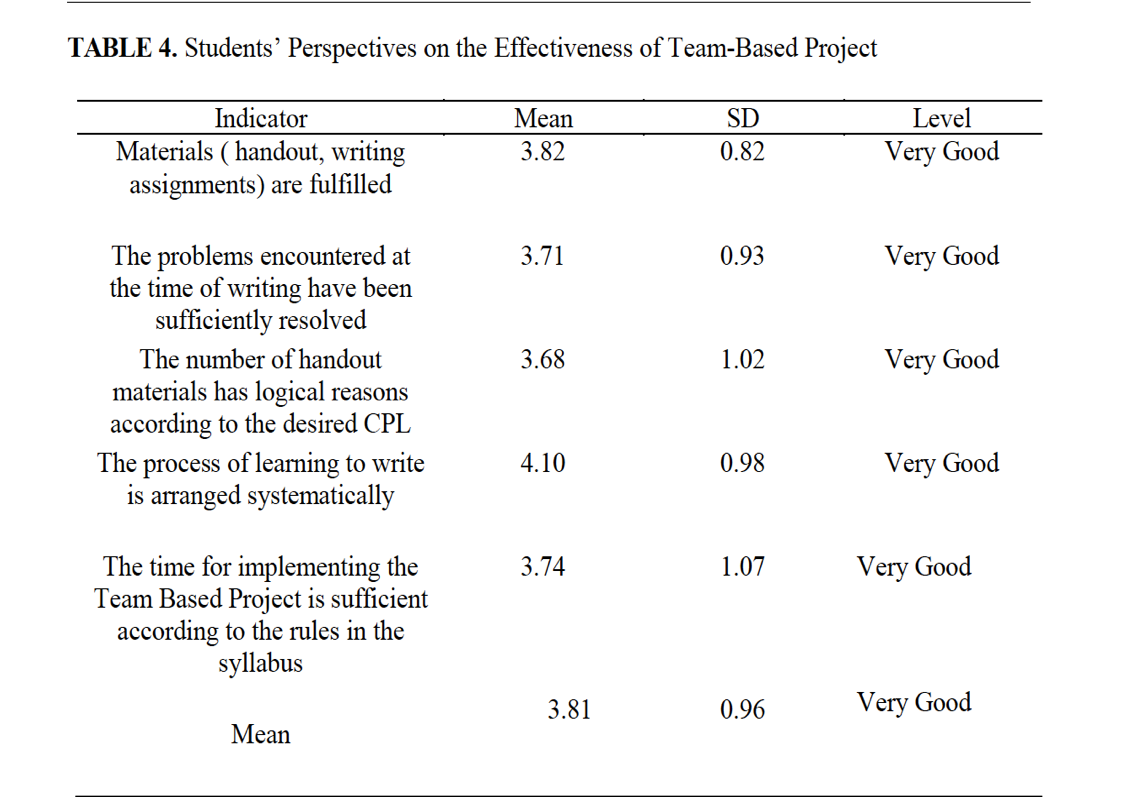
- The student perspectives on learning through Team-Based Projects are divided into four: student perspectives on motivation and their writing results, student perspectives on the effectiveness of Team-Based Projects, student perceptions of independent learning through Team-Based Projects and Hybrid understanding, and student perceptions about working in groups.
- The lecturers should apply hybrid learning and team-based projects to motivate and train students to learn independence and provide experiences of a harmonious learning process. Next, for future researchers, it is advisable to expand the research subject so that the results obtained are more in-depth and can be implemented in other English skills, namely speaking, listening, and reading.
Downloads
References
Alsowat, H. H. (2022). Hybrid learning or virtual learning? effects on students’ essay writing and digital literacy. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 13(4), 872–883. https://doi.org/10.17507/jltr.1304.20
Alwasilah, S. S. (2019). Creating your animated stories with plotagon: Implementation of project-based learning in narrative writing. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 18(12), 333–349. https://doi.org/10.26803/ijlter.18.12.19
Aslam, M. Z., Hakeem Barzani, S. H., Aslam, T., & Rasool, U. (2021). Teachers and students perceptions towards online ESL classrooms during covid-19: An empirical study in North Cyprus. Journal of Asia TEFL, 18(4), 1423–1431. https://doi.org/10.18823/asiatefl.2021.18.4.22.1423
Banditvilai, C. (2016). Enhancing students’ language skills through blended learning. The Electronic Journal of E-Learning , 14(3), 220–229. www.ejel.org
Baresh, E. F., Ali, S. M., & Darmi, R. (2019). Using hybrid problem-based learning (HPBL) approach to enhance Libyan EFL students’ engagement with English language. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 7(2), 9–20. https://doi.org/10.7575/aiac.ijels.v.7n.2p.9
Baresh, E. F., Ali, S. M., Ii, A., & Darmi, R. (2018). Motivating the Libyan English as foreign language speaker students through the hybrid problem based learning approach. International Journal of Islamic Studies, 10(2), 2289–9944. http://al-qanatir.com
Cheadae, A., & Khongput, S. (2019). Thai EFL students’ perceptions toward learning English descriptive paragraph writing through problem-based learning. Veridian E-Journal, Silpakorn University, 12(6), 1688–1704.
Cresswell, J. W. (2014). Research design, qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods approaches. Sage Publications.
Cresswell, J. W., & Plano, C. V. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed methods research (3rd ed.). Sage Publications.
Gulnaz, F., Althomali, A. D. A., & Alzeer, D. H. (2020). A Gender-Based Study to Investigate Saudi Male and Female EFL Learners’ Satisfaction Towards the Effectiveness of Hybrid Learning. International Journal of English Linguistics, 10(5), 321. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijel.v10n5p321
Guo, P., Saab, N., Post, L. S., & Admiraal, W. (2020). A review of project-based learning in higher education: Student outcomes and measures. International Journal of Educational Research, 102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101586
Heim, K. (2022). Designing hybrid learning spaces together: The potential of cooperative projects for language teacher education. Anglistik, 33(1), 185–201. www.tcpdf.org
Jalinus, N., Nabawi, A., & Mardin, A. (2017). The seven steps of project based learning model to enhance productive competences of vocational students. Advances in Social Science, Education, and Humanities Research, Vol.102, 251–256.
Kassem, M. A. M. (2018). Improving EFL students’ speaking proficiency and motivation: A hybrid problem-based learning approach. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 8(7), 848. https://doi.org/10.17507/tpls.0807.17
Kornilov, I. v., Danilov, D. A., Kornilova, A. G., Golikov, A. I., & Gosudarev, I. B. (2020). Different approaches to the development of online learning in higher education. Propósitos y Representaciones, 8(SPE3), e706. https://doi.org/10.20511/pyr2020.v8nspe3.706
Lee, H. J., Kim, H., & Byun, H. (2017). Are high achievers successful in collaborative learning? An explorative study of college students’ learning approaches in team project-based learning. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 54(5), 418–427. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2015.1105754
Lukas, B. A., & Yunus, M. M. (2021). ESL teachers’ challenges in implementing e-learning during COVID-19. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 20(2), 330–348. https://doi.org/10.26803/IJLTER.20.2.18
Lynch, L. C. Y. (2014). Blending Online Asynchronous and Synchronous Learning. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 15(2), 189–212.
Maulida, U. (2020a). Konsep blended learning berbasis Edmodo di era new normal. Dirasah, 2(2), 121–136.
Maulida, U. (2020b). Konsep blended learning berbasis edmodo di era new normal. Dirasah, 2(2), 121–136.
Purnomo, A., Ratnawati, N., & Aristin, N. F. (2016). Pengembangan pembelajaran blended learning pada generasi z. Jurnal Teori Dan Praksis Pembelajaran IPS, 1(1), 70–77.
Reese, S. A. (2015). Online learning environments in higher education: Connectivism vs. dissociation. Education and Information Technologies, 20(3), 579–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-013-9303-7
Santikarn, B., & Wichadee, S. (2018). Flipping the classroom for English language learners: A study of learning performance and perceptions. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 13(9), 123–135. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v13i09.7792
Soliman, N. A. (2014). Using e-learning to develop EFL students’ language skills and activate their independent learning. Creative Education, 05(10), 752–757. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2014.510088
Stein, J., & Graham, C. R. (2020). Essentials for blended learning a standards-based guide (Second Edition). Routledge.
Suh, Y. M., & Huh, S. (2017). Korean university readers’ growth through an integrated approach of conventional and critical literacy. English Teaching, 72(4), 23–51. https://doi.org/10.15858/engtea.72.4.201712.23
Sumarno, W. K., & Tatik, T. (2018). Integrating edmodo-based digital portfolio with EFL writing instruction: Exploring the students’performance. Journal of English Education, 3(2), 100–106. https://doi.org/10.31327/jee.v3i2.864
Sun, A., & Chen, X. (2016). Online education and its effective practice: A research review. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 15(1), 157–190. http://www.informingscience.org/Publications/3502
Titova, S. (2017). The use of MOOC as a means of creating a collaborative learning environment in a blended CLIL course. In CALL in a climate of change: adapting to turbulent global conditions – short papers from EUROCALL 2017 (pp. 306–311). Research-publishing.net. https://doi.org/10.14705/rpnet.2017.eurocall2017.731
Tsiakyroudi, M. (2018). Exploring the effectiveness of Edmodo on Greek EFL B1 learners’ motivation to write. Research Papers in Language Teaching and Learning, 9(1), 96–112. http://rpltl.eap.gr
Tusino, Sukarni, S., & Rokhayati, T. (2021). Hybrid Synchronous and Asynchronous Language Learning in Writing Class: The Learners’ Psychosocial Perspectives in Indonesia. New Educational Review, 65, 190–199. https://doi.org/10.15804/tner.2021.65.3.15
Villalba, S. M. (2022). Blogging in action: Teaching English within the project-based learning approach. Computer Assisted Language Learning Electronic Journal (CALL-EJ), 23(1), 63–77.
Wang, Q., Quek, C. L., & Hu, X. (2017). Designing and improving a blended synchronous learning environment: An educational design research. International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 18(3), 99–118. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v18i3.3034
Wang, S., & Seepho, S. (2017). Facilitating Chinese EFL learners’ critical thinking skills: The contributions of teaching strategies. SAGE Open, 7(3), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244017734024
Wijayatiningsih, T. D. , Bharati, D. A. L. , Faridi, A. , &, & Fitriati, S. W. (2021). Students ’ voices on implementing blended synchronous learning In teaching genre- based writing. Proceeding of the Sixth International Conference of Science, Education, and Technology (ISET) 2020, 574(Iset 2020), 700–704.
Wijayatiningsih, T. D., Bharati, D. A. L., Faridi, A., & Fitriati, S. W. (2022). Scaffolding for learners’ writing literacy through blended learning in an Indonesian EFL context. Journal of Asia TEFL, 19(1), 336–344. https://doi.org/10.18823/asiatefl.2022.19.1.26.336
Williams, L. , & Lahman, M. (2011). Online discussion, student engagement, and critical thinking. Journal of Political Science Education, 7(2), 143–162.
Wilson, A. (2020). Penerapan metode pembelajaran daring (online) melalui aplikasi berbasis android saat pandemi global. SAP (Susunan Artikel Pendidikan), 5(1), 66–72. https://doi.org/10.30998/sap.v5i1.6386
Wright, B. M. (2017). Blended learnings student perception of face-to-face and online EFL lessons. Indonesian Journal of Applied Linguistics, 7(1), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.17509/ijal.v7i1.6859
Yang, Z., & Spitzer, L. (2020). A case for hybrid learning: Using a hybrid model to teach advanced academic reading. ORTESOL Journal, 37, 11–22.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Testiana Deni Wijayatiningsih, Muhammad Muhibbi, Dodi Mulyadi, J-Roel B.Semilla

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







