Internal continuatives and logical metaphors: A development of classifying conjunctive relation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v6i2.1360Keywords:
external, internal, conjunctive relation, genre, stage, phaseAbstract
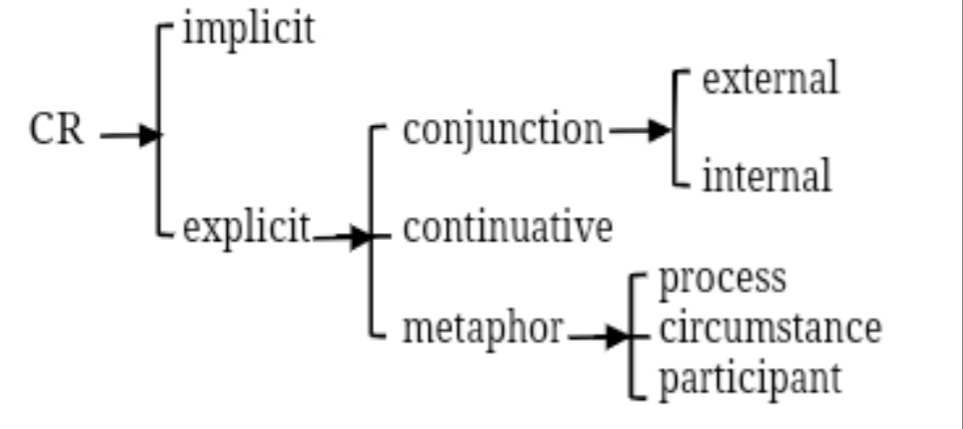
This research attempts to develop Martin’s & Rose’s concept of conjunctive relation (CR) analysis, in which the external and internal roles of conjunction do not include the other two types of conjunctive relation markers such as continuative and logical metaphor. Relying on more than twenty international journal articles, the research findings exhibit that certain types of continuative and logical metaphor can not only operate externally to connect events and qualities but they can also function internally to organize evidences and arguments in texts. As a result, not only a new role of internal continuative and logical metaphor can be confirmed, but the findings will also introduce an elaborated development of classifying CR in general. The emergence of the internal role of continuative and logical metaphor leads to a more elaborate way of connecting and grouping clauses into different units of discourse. In this way, they will also be able to demonstrate how texts can be built up through clauses, phases, and stages in a particular genre, without the need to be interpreted in conjunctions.
HIGHLIGHTS:
- This article attempt to find a new way of classifying internal and external conjunctive relation that is comprised of conjunction, continuative and metaphor. Martin (2007) argues that only conjunction that perform external and inter.
- This article exhibits that actually external and internal roles can also be performed by continuative and metaphor.
- Some types of logical metaphors and continuations can not only operate externally to connect events and qualities, but can also function internally to organize evidence and arguments in a text.
Downloads
References
Alyousef, H. S. (2016). A multimodal discourse analysis of the textual and logical relations in marketing texts written by international undergraduate students. Functional Linguistics, 3(1), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40554-016-0025-1
Darmi, R. & Albion, P. (2014). A review of integrating mobile phones for language learning. Paper presented at the 10th International Conference Mobile Learning. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED557201
Devrim, D. Y. (2015). Grammatical metaphor: What do we mean? What exactly are we researching? Functional Linguistics, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40554-015-0016-7
Dreyfus, S., & Bennett, I. (2017). Circumstantiation: taking a broader look at circumstantial meanings. Functional Linguistics, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40554-016-0036-y
Grbich, C. (2007) Qualitative data analysis: An introduction. London: Sage Publication.
Halliday, M. A. K., & Matthiessen, C. M. I. M. (2013). Halliday’s introduction to functional grammar: Fourth edition. In Halliday’s Introduction to Functional Grammar: Fourth Edition. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203431269
Hasan, R. (2014). Towards a paradigmatic description of context: Systems, metafunctions, and semantics. Springer: Functional Linguistics. 1 (9). 1-54.
Ignatieva, N., & Rodríguez-Vergara, D. (2015). Verbal processes in academic language in Spanish: exploring discourse genres within the systemic functional framework. Functional Linguistics, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40554-015-0014-9
Jan, J. M. & Omar, Nor A. M. (2013). Humour in meetings: A case study of power in the Malaysian academic context. Pertanika: Social Sciences and Humanities. 21 (S). 103 – 116.
Lecompte-Van Poucke, M. (2016). Exploiting the ‘non-dit’ and other discursive tactics in the New Caledonian independence debate: a pragma-functional approach to critical discourse analysis. A SpringerOpen Journal: Functional Linguistics. 3 (2). 1-30.
Lee, I. (2012). Genre-based teaching and assessment in secondary English classrooms. English teaching: Practice and Critique. 11 (4). 120-136.
Liddicoat, A.J. (2009). Communication as culturally contexted practice: A view from intercultural communication. Australian Journal of Linguistics. 29 (1). 115-133.
Martin, J.R., & Rose, D. (2007). Working with discourse: meaning beyond the clause. In British Library Catalogoing (Vol. 20, Issue 1). https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-44502004000100011
Martin, J. R. (2014) Evolving systemic functional linguistics: beyond the clause. A SpringerOpen Journal: Functional Linguistics. 1 (3). 1-24.
Martin, J.R. (2008). Incongruent and proud: de-vilifying ‘nominalization’. Discourse & Sciety. 9 (6). 827–836.
Martin, James R. (2014). Evolving systemic functional linguistics: beyond the clause. Functional Linguistics, 1(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2196-419x-1-3
Martin, J.R., Matthiessen, C.M.I.M., & Painter, C. (2010). Deploying Functional Grammar. Beijing: The Commercial Press.
Martin, J. R. Martin & Rose, D. (2007). Working with discourse: meaning beyond the clause. Bloomsbury.
Matthiessen, C.M.I.M., Kashyap, A.K. (2014). The construal of space in different registers: an exploratory study. Language and Science. 45. 1-27.
Matthiessen, C.M.I.M. (2015a) Register in the round: registerial cartography. A SpringerOpen Journal: Functional Linguistics. 2 (9). 1-48.
Matthiessen, C.M.I.M (2015b) Modelling context and register: the long-term project of registerial cartography. Letras, Santa Maria. 25 (50). 15-90.
Nababan, M.R., Santosa, R., Budiharjo, B. & Dzakiria , H. (2016). Eliciting genre-based translation model from Indonesian into English. Advanced Science Letters, 22 (12) 4444- 4447.
Naderi, S., Yuen, Chee Keong, & Latif, Hafizah. (2013). Conjunctive ties in conference proceeding of EFL Persian graduate students. Social Sciences & Humanities. 21 (s). 13-28.
Porcu, G., Roger, V., Jacquier, A., Mazouni, C., Rojat‐Habib, M. C., Girard, G., ... & Gamerre, M. (2005). Uterus and bladder necrosis after uterine artery embolisation for postpartum haemorrhage. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 112(1), 122-123.
Santosa, R. (2011). Logika wacana: Analisis hubungan konjungtif dengan pendekatan LSF. Surakarta: UNS Press.
Santosa, R. (2010). Bentuk dan makna metafora logikal dan pengaruhnya terhadap gaya bahasa. Kajian Linguistik Dan Sastra, 22(2), 183–192.
Santosa, R., Priyanto, A. D., & Nuraeni, A. (2011). Genre and Register of Antagonist’s Language in Media: An Appraisal Study of Indonesian Newspapers. Kata, 16(1), 23–36. https://doi.org/10.9744/kata.16.1.23-36
Santosa, R., Priyanto, A.D., Nuraeni, A., & Dzakiria, H. (2016). The language of mass street protests in Indonesia. Advance Science Letters. 22 (16). 4393-4396.
Santosa, R., Priyanto, A.D., & Nuraeni, A. (2014). Genre and register of antagonist’s language in media: An appraisal study of Indonesian newspapers. Kata. 16 (1). 23-36
Santosa, R., Priyanto, D.P., & Nuraeni, A. (2011). Bahasa demokratis dalam media televisi Indonesia. Lingua: Jurnal Bahasa dan Sastra. 6 (3). 227-240.
Spradely, J.P. (2007). Metode etnografi (M. Z. Elizabeth, Trans.) (2nd Ed.). Yogyakarta: Tiara Wacana.
Stuart-Smith, V. (2007). The hierarchical organization of text as conceptualized by rhetorical structure theory: A systemic functional perspective. Routledge: Australian Journal of Linguistics. 27 (1). 41-61.
Taboada, M. (2011). Stages in an online review genre. Text and Talk, 31(2), 247–269. https://doi.org/10.1515/TEXT.2011.011
Trebits, A. (2009). The most frequent phrasal verbs in English language EU documents–A corpus-based analysis and its implications. System, 37(3), 470-481.
Verikaite, Daiva. (2005). Variations of conjunctive discourse markers across different genres. Zmogus ir Zodis. 7 (3). 68-75.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Riyadi Santosa, Sumarlam, Tri Wiratno, Agus Dwi Priyanto, Ratna Susanti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







