Affective factors and eustress-distress of nursing English students: A comparison analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21070/jees.v8i1.1711Keywords:
eustress-distress, anxiety, self-efficacy, learning performanceAbstract
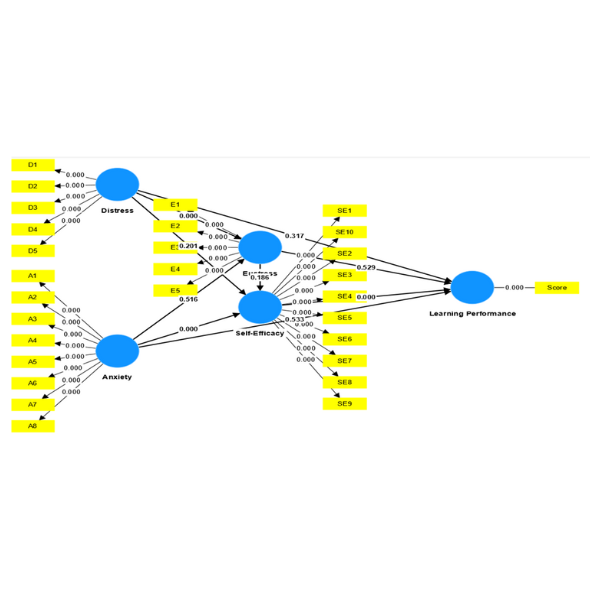
Studies outside of cognitive aspects, especially on psychological and affective factors, still have limited findings. In fact, these two issues contribute greatly to the success of English for Academic Purposes (EAP). This study aims to identify level of eustress-distress, anxiety-self-efficacy, and comparisons between these variables on learning performance of nursing students. This study used a mixed-method, a comparative study using closed and open questionnaires, and EAP reading test to 95 nursing students in the program of EAP. Certainly, the analysis used correlation and comparison tests using PLS-SEM and qualitative analysis of open questionnaires. The results showed that level of eustress-distress, and anxiety-self-efficacy of students were quite satisfactory. This means that students have ability to adapt positive reactions to learning pressure, more enthusiastic, and develop good self-confidence. Although distress does not influence self-efficacy and learning performance, it does have a significant impact on eustress. There is a strong impact and correlation between anxiety on self-efficacy, and self-efficacy on learning performance. So self-efficacy shows a strong moderating variable to bridge anxiety and learning performance. Qualitative findings also show that there are internal and external factors that contribute to the growth of eustress and self-efficacy. Further recommendations on these findings are also presented at the end of this study.
HIGHLIGHTS:
- Affective factors are psychological constructs related to personality that impact foreign language mastery and provide benefits to language learning methodologies. Affect refers to feelings or emotions, including anxiety, self-esteem, motivation, attitude, and personality traits. The affective factors that influence language input are often referred to as "affective filters.”
- Eustress is an adaptation process in which an organism survives by changing its behavior and circumstances, to increase buffer zone, and result in an increase in the body's adaptive abilities. In simple terms, eustress is a positive adaptive response to a stressor by individuals.
- Distress is an unpleasant or negative emotional reaction to stress. Often students experience stress and psychological pressure due to an increase in burden of academic performance and personal factors, for example associating with new peer groups.
Downloads
References
Anwar, K. (2016). Panel Discussion and the Development of Students’ Self Confidence. English Language Teaching, 9(4), 224. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v9n4p224
Anwar, K., Wardhono, A., & Budianto, L. (2022). Cypriot Journal of Educational Attitude and social context in MALL classes: A view from midwifery learners. 17(9), 3048–3066. https://doi.org/10.18844/cjes.v17i9.7332
Bao, Y., & Liu, S. (2021). The Influence of Affective Factors in Second Language Acquisition on Foreign Language Teaching. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 09(03), 463–470. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2021.93030
Bienertova-Vasku, J., Lenart, P., & Scheringer, M. (2020). Eustress and Distress: Neither Good Nor Bad, but Rather the Same? BioEssays, 42(7), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201900238
Bourgeois, T. J. (2018). Effect of Eustress, Flow, and Test Anxiety on Physical Therapy Psychomotor Practical Examinations TT - Efecto de la ansiedad por esfuerzo, flujo y prueba en la fisioterapia Exámenes psicomotores prácticos. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses, 217. https://manchester.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.proquest.com/docview/2138186804?accountid=12253%0Ahttp://man-fe.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/openurl/44MAN/44MAN_services_page?genre=dissertations+%26+theses&atitle=&author=Bourgeois%2C+Todd+J.&volume=&
Branson, V., Dry, M. J., Palmer, E., & Turnbull, D. (2019). The Adolescent Distress-Eustress Scale: Development and Validation. SAGE Open, 9(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019865802
Casali, N., Ghisi, M., Rizzato, R., Meneghetti, C., & De Beni, R. (2022). Validation of the “Study-Anxiety” Questionnaire: a scale for the initial assessment of university students seeking psychological help. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-022-09982-8
Courtney, L., Graham, S., Tonkyn, A., & Marinis, T. (2017). Individual Differences in Early Language Learning: A Study of English Learners of French. Applied Linguistics, 38(6), 824–847. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amv071
Crookes, G. V., & Ziegler, N. (2021). Critical language pedagogy and task-based language teaching: Reciprocal relationship and mutual benefit. Education Sciences, 11(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060254
Gallagher, H. C. (2013). Willingness to communicate and cross-cultural adaptation: L2 communication and acculturative stress as transaction. Applied Linguistics, 34(1), 53–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/ams023
Getie, A. S. (2020). Factors affecting the attitudes of students towards learning English as a foreign language. Cogent Education, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2020.1738184
Gibbons, C., Dempster, M., & Moutray, M. (2008). Stress and eustress in nursing students. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 61(3), 282–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04497.x
Hashemi, M. (2011). Language stress and anxiety among the English language learners. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 30(May), 1811–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.349
Hwang, G. J., Hsu, T. C., Lai, C. L., & Hsueh, C. J. (2017). Interaction of problem-based gaming and learning anxiety in language students’ English listening performance and progressive behavioral patterns. Computers and Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.11.010
Ifdil, I., Bariyyah, K., Dewi, A. K., & Rangka, I. B. (2019). The College Academic Self-Efficacy Scale (CASES); An Indonesian Validation to Measure the Self-Efficacy of Students. Jurnal Kajian Bimbingan Dan Konseling, 4(4), 115–121. https://doi.org/10.17977/um001v4i42019p115
Illyin, I., Hanifah, G. N., & Yunianti, S. (2021). The affective factors influencing students’ speaking ability. UAD TEFL International Conference, 2, 146. https://doi.org/10.12928/utic.v2.5749.2019
Khodadad, M., & Kaur, J. (2016). Causal relationships between integrative motivation, self-efficacy, strategy use and English language achievement. 3L: Language, Linguistics, Literature. https://doi.org/10.17576/3L-2016-2203-08
Kissau, S. (2012). Perceptions of self-efficacy for two types of second language methods instruction. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 25(4), 295–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2011.587436
Kormos, J., Kiddle, T., & Csizér, K. (2011). Systems of goals, attitudes, and self-related beliefs in second-language-learning motivation. Applied Linguistics, 32(5), 495–516. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amr019
Li, C. T., Cao, J., & Li, T. M. H. (2016). Eustress or distress: An empirical study of perceived stress in everyday college life. UbiComp 2016 Adjunct - Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, September, 1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1145/2968219.2968309
Marten, F. (2017). The mediating effect of eustress and distress on the relation between the mindset towards stress and health. Mediating Effect of Eustress and Distress, 1–22. https://essay.utwente.nl/72588/1/MARTEN_BA_BMS.pdf
Mehta, K. J., Miletich, I., & Detyna, M. (2021). Content-specific differences in padlet perception for collaborative learning amongst undergraduate students. Research in Learning Technology, 29(1063519), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v29.2551
Ni, H. (2012). The effects of affective factors in SLA and pedagogical implications. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 2(7), 1508–1513. https://doi.org/10.4304/tpls.2.7.1508-1513
Punam, D., & Washington, A. (2015). Impact of stress on work performance and career development – application of Herzberg’ S theory for handling stress effectively. International Journal of Education and Research, 3(6), 127–138.https://www.ijern.com/journal/2015/June-2015/10.pdf
Rajabi, P., Mahmoodi, K., & Hosseini, S. A. (2021). Flipped classroom model and its impact on Iranian EFL learners’ classroom anxiety and listening performance. Call-Ej, 22(3), 1–16. http://callej.org/journal/22-3/Rajabi-Mahmoodi-Hosseini2021.pdf
Rudland, J. R., Golding, C., & Wilkinson, T. J. (2020). The stress paradox: how stress can be good for learning. Medical Education, 54(1), 40–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13830
Sinclair, A. H. (2018). Department of Psychology Department of Psychology. Fall, 1–7. https://ir.canterbury.ac.nz/handle/10092/7014
Yahya, A., Said, Y. R., & Masruddin. (2019). Developing appropriate english learning materials for syariah economic law study program students at iain palopo, Indonesia. Asian ESP Journal, 15(1), 22–33. http://repository.iainpalopo.ac.id/id/eprint/1636/1/Developing%20approriate%20english%20learning%20material%20for%20syariah%20economy%20law%20study%20program.pdf
Zayed, J., & Al-Ghamdi, H. (2019). The Relationships Among Affective Factors in Learning EFL: A Study of the Saudi Setting. English Language Teaching, 12(9), 105. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v12n9p105
Zhu, B., & Zhou, Y. (2012). A study on students’ affective factors in Junior high school English teaching. English Language Teaching, 5(7), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v5n7p33
Zulfikar, T., Dahliana, S., & Sari, R. A. (2019). An Exploration of English Students’ Attitude toward Learning English. English Language Teaching Educational Journal, 2(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.12928/eltej.v2i1.947
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Khoirul Anwar, Nirwanto Maruf , Yudhi Arifani , Marwa Mansour

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







